Deforestation – a serious threat to Pakistan climate, a case study from “Swat” through remote sensing and GIS: The forest resources are one of the most basic resources worldwide.

Forest play a vital role in keeping world ecological balance and constitute reliable global natural resources which are depleting and degrading worldwide. Pakistan is considered as a developing country having scarcity of forest resources.
The total area cover in Pakistan is about 1687 ha which cover 2 percent of total area (FAO). In Pakistan, the deforestation rate is approximately 0.5% per year, which is high and horrifying. Deforestation and Forest degradation are considering as the most concerning environmental problem.

The issue linked to forest land use land cover changes is an essential subject to be studied at global and regional level, deforestation and forest degradation has become a major issue in last few decades. This has become attentive in international level because of concern over issues such as global warming and climate change.
The decline in forest area has also become intractable for planner and researcher due to such problems. Moreover, consuming of forest lands to other land use and illicit cutting were increased recently in alarming rate in worldwide mostly in Pakistan.
The rapid growth in population leads many problems in the world and the most significant impact on biodiversity. The study showed that there are some landscapes on globe which remain in original state.The climate change and anthropogenic activities have altered land forms in some manners. Land use land cover harshly affects the natural environmental components with the passage of time.
This study conducted in Elum marghuzar valley, Swat district. Elum Marghuzar is situated in the northern district Swat located in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. Swat is famous for its green beauty, snowy peaks, fertile land, green pastures, waterfalls and beautiful tourist spots.
Swat valley is also called as Switzerland of Pakistan due to rich biodiversity, fresh streams and river, lakes, high mountains and large forest cover. There are millions of tourists visiting Swat per annum.Swat valley covered the huge forests and plantations. The vegetation types in the area are subtropical, temperate and alpine forest.
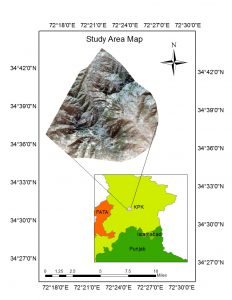
Swat district has witnessed remarkable expansion, growth and developmental activities such as road construction, infrastructures, shifting of forest lands and many other anthropogenic activities mostly tourism development from 2010.The total population of district Swat is more than 2.3 million and covers 274,620 households with annual population growth of 3.2 percent from 1998 (2017 census) which is considered high threat for district.
AIMS AND OBJECTIVES:
Aims
The study aims to produce forest land cover maps of Elum Marghuzar valley at different years in order to detect the changes that have taken place particularly in forested land during two decades and subsequently predict likely changes that might take place in the same over periods in near future.
Objectives
The following specific objectives will peruse for the achievement of above aims.
- To map the classification scheme of forest land.
- To carried out the decline rate of Forest area.
- To determine drivers or factors which lead to replaced Forest land.
For obtaining of optical satellite data of Elum Marghuzar valley in northern province KPK, the month September is selected to be the most suitable due to least amount of cloud and snow cover within this period. The entire archive was observed and examined carefully to observe the images taken throughout in October month. Remotely sensed data for deforestation and forest cover were obtained for three years 1997, 2007 and 2017 shown in table1.
The data were obtained from united state geographical survey (USGS) comprises of Landsat 5 ETM with spatial resolution of 30m having 4 bands and each including 3770 lines and 4223 samples. Landsat 7 ETM + having spatial resolution of 30m consist of 4 band and each band comprises of 7001 lines and 7761samples.landsat spatial resolution of Landsat 8 OLI is 30m consist of 4 bands each comprises 7981 lines and 7841 samples shown in table 1.
Table3.1 : Landsat Data Used In This Study
S.no | Platforms | Periods | Number of bands | Data size per band (pixels) | Spatial resolution |
1 | Landsat-5 (ETM) | 1997 | 4 | 1334×1511 | 30m |
2 | Landsat-7 (ETM+) | 2007 | 4 | 1334×1511 | 30m |
3 | Landsat-8 (OLI) | 2017 | 4 | 1334×1511 | 30m |
This study concluded the forest land cover in years 1997, 2007 and 2017 based on the combine integration of remote sensing and GIS.
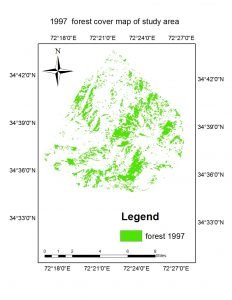
The study shows that the valley was pre-dominated by rich forest resources which were generally consumed by urban expansion and agriculture extension. The study revealed that the forest area has decreased about 1641 hectares which is the 47.29 %. The total forest area were recorded 3470.21 hectare (20.19%) , 2991.04 hectare (17.40%) and 1829.12 hectares (10.64%) in total area of 17186 hectares in years 1997, 2007, 2017, respectively. The results indicates that forest area were much decrease in 2007-2107 than 1997-2007 because of urban expansion and cultivation lands extension.
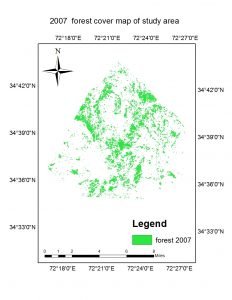
The annual deforestation was 82.05 hectares which is 2.36 % of the total forest area. It means that we will loss 82.05 hectares 2.36 % of land every year. It is estimated that in next 23 years we will loss all forest area in the valley if this rate of deforestation remain continue.
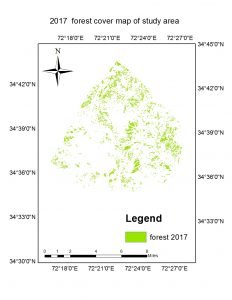
The results indicate that the anthropogenic activities were responsible for heavy forest loss in last two decades. The expansion of built-up areas and agricultural land were basic drivers of deforestation. The illegal timber extraction, poor land management and monitoring of forest resources were also contributed on forest degradation.This study also shows the scarcity of energy resources and awareness which compel the population to use the fuel wood from the forest.
RECOMMENDATIONS:
The following measure for reduction of deforestation and forest degradation are essential to preserve and conserve natural resources. The particular organization must show responsibility for the conservation and preservation of natural resources. The lack of proper management and improper land use in the valley cause heavy declines in forest area. We put some of the following measures which could asses to control degradation of natural resources and deforestation.
The first drivers that were responsible for heavy forest loss were urban expansion and cultivation land extension which need proper land use management and Environmental impact assessment (EIA). The government and particular department must provide proper measures for infrastructures and urban expansion, promote awareness and realize importance of forest resources.
The regeneration and plantation like Billion Trees Afforestation Project (BTAP) was initiated in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa which play a key role in province particularly in this valley. Hundreds of plants were seen to be newly planted in the area. The ten billion trees afforestation project from federal government which is known as clean and green Pakistan program has started recently throughout the country that is quite well to improve forest area but the area still need to enhance more regeneration under such program.