ARTIFICIAL SEED is an encapsulation of somatic embryo, shoot buds or aggregates of a cell or any tissues which have the ability to form a plant in in-vitro or ex vivo condition. Artificial seed is a promising technique for the propagation of transgenic plants, polyploids with elite traits non-seed producing plants and plant lines that has a problem in seed propagation. Artificial seed is clonal technique and it cuts short the laborious procedure of conventional recombination breeding and can bring the advancements of biotechnology to the doorsteps of a farmer in a cost effective way.
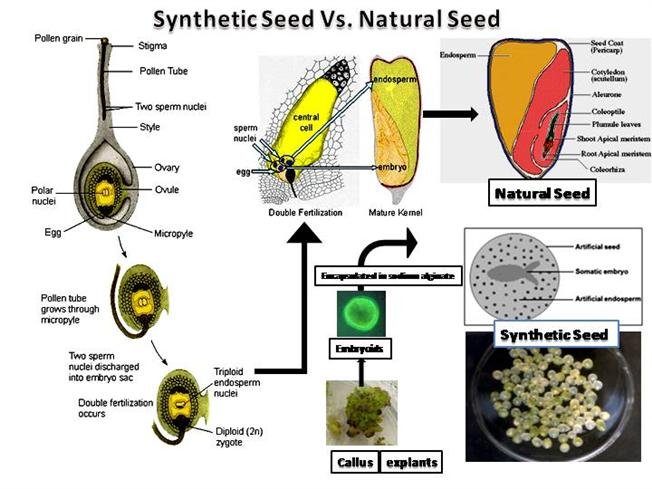
A seed is basically a zygotic embryo with food storage tissue (endosperm) and covered with a protective layer and this layer protects the seed against desiccation and increases its durability and protects it against external damages. Seeds with zygotic embryo are a combination of sexual reproduction between two parents. After the discovery of somatic embryogenesis in 1950 now it was possible to have the alternate of conventional zygotic seeds. Somatic embryo produces from the somatic cell of a single parent. They differ from zygotic embryo because are produced in in-vitro culture technique without protective coats and they do not become quiescent.
There could a number of systems of artificial seed production but most economically feasible is shown in the diagram. It involves the selection of explant from the choice of plants. After that in the laboratory using tissue culture techniques callus is induced in the explants. In next step, the somatic embryo is induced in callus using tissue culture techniques.
Next step is the optimization of the clonal production system followed by the development of mature embryos that are capable of converting into mature plants. After that differentiation and maturation of somatic embryo is followed.
After that mature embryos induce to quiescence, development of encapsulation and coating system and its optimization and conversion requirements for field growth and greenhouse (Fertilization, watering and transplanting etc) are followed.
There are many advantages of artificial seeds. One of the main advantages is large scale propagation and a variety of genotypic plantations. It is also an important to a source of germplasm conservation of superior, extinct and endangered species. Artificial seeds are easy to handle, transport and transport charges are very low due to their small size. In addition during the production of artificial seed, one can study seed coat formation, a fusion of endosperm in embryo development and seed germination. Synthetic seed production is cost effective when compared to traditional method.