Uncontrolled growth of cells is called cancer. A type of cancer that concerns with the lungs is known as lung cancer. Among cancer deaths lung cancer is a leading disease as compare to breast, colon and prostate cancer combined.

Risks of lung cancer development increase with smoking. It has two types, one is small cell lung cancer and the other one is non-small cell lung cancer, according to the type of cells that are affected by this disease. 
Types
Lung cancer has two types according to the appearance of cells under microscope during examination. Treatment of the patient is decided according to the type of lung cancer.
- Small cell lungs cancer
This type of disease mostly develops in heavy smoker and this is less common then non- small cell lung cancer
- Non-small cell lungs cancer
This is an umbrella term used for different types of lung cancer that shows similar behavior. This lungs cancer includes large cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
Prevalence
Lung cancer related deaths are more common worldwide and in USA. Nearly 160,000 patients die in USA alone and 220,000 new cases have been diagnosed. This is most common type of cancer then prostate, colon and breast cancer.
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of lung cancer may include:
- Cough
- Chest pain
- Bone pain
- Hoarseness
- Weight loss
- Coughing up blood, even a small amount
- Shortness of breath
- Headache
Causes
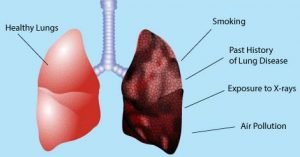
Cigarette smoke is the major cause of lung cancers, affects smoker and people who exposed to the smoke. It also develops in people who never smoked and had no prolonged exposure to the second hand smoke.
Risk Factors
- Interstitial lung diseases
- Smoking
- Exposures to carcinogens and asbestos
- Exposure to radon gas
- Family history of lung cancer
- Exposure to second hand smoke
Diagnoses
Imaging test: An X-ray image shows abnormal mass where as CT scan is also performed to detect small lesions
Sputum cytology: Microscopic examination of sputum reveals the presence of lung cancer cells.
Tissue biopsy: A small sample of affected cells is removed for detailed examination and the procedure is known as biopsy.
Treatment
Lung cancer surgery
According to the health and stage of the cancer, doctor decides the best treatment. In some cases risk of side effects seems to be increased then doctor decides to cure symptoms of the disease.
Procedures to remove lung cancer include:
- Wedge resection
- Segmental resection
- Lobotomy
- Pneumonectomy

Radiation therapy
High energy power beam of X-ray and proton is used to kill cancerous cells
Chemotherapy
This treatment includes drugs that kill the cancerous cells which were remaining after surgery
Radiosurgery
This is an intense radiation therapy performed in patients who can’t undergo surgery.
Targeted drug therapy
This therapy mainly focuses on specific abnormalities present within the lung cancer cells.
Immunotherapy
In this treatment immune system is used against cancer cells mostly used for advanced lung cancer
Prevention
- Risk factors can be reduced by:
- Avoid smoking
- Check radon in home
- Avoid carcinogens at work place
- Eat more fruits and vegetables
- Include exercise in daily routine
Conclusion
Lung cancer is a major death causing disease, only 16% results have been achieved in last 5 years. It is examined by CT scan, sputum examination, biopsy and X-ray. Its main treatments include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, Radiosurgery, targeted drug therapy, surgery and radiation therapy.
References:
Clay, R., Maldonado, F. and Edell, E.S., 2018. Lung cancer screening. In Interventions in Pulmonary Medicine (pp. 313-322). Springer, Cham.
Whittaker, S.A., Padilla, M.L., Mhango, G., Powell, C.A., Henschke, C., Yankelevitz, D., Salvatore, M., de Torres, J.P. and Wisnivesky, J.P., 2018. Interstitial Lung Abnormalities as an Independent Risk Factor for Lung Cancer. In D99. CLINICALLY INFORMATIVE BIOMARKERS IN LUNG CANCER: A NEEDLE IN A HAYSTACK (pp. A7416-A7416). American Thoracic Society.
Shue, Y.T., Lim, J.S. and Sage, J., 2018. Tumor heterogeneity in small cell lung cancer defined and investigated in pre-clinical mouse models. Translational lung cancer research, 7(1), p.21.
Authors: Lubna Majeed, M. Naeem Faisal, Aisha Mahmood, Noreen Aslam
Institute of Pharmacy, Physiology and Pharmacology, University of Agriculture Faisalabad, Pakistan
Corresponding Author: lubna.majeed384@gmail.com