HD1 is much sufficient that its mild is estimated to be 13.5 billion years previous, or simply 300 million years after the Huge Big Bang.
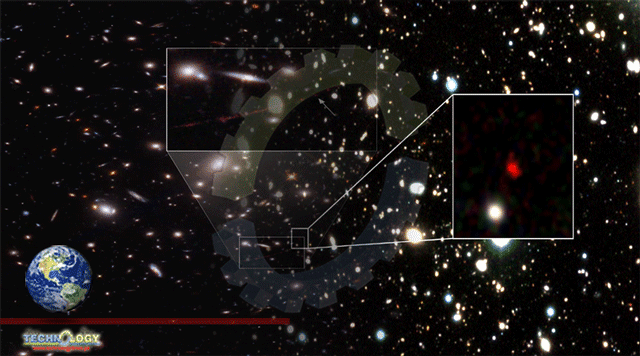
It has been few weeks for recognizing distant objects within the universe. As Forbes notes, Japanese researchers have detected what could be essentially the most distant galaxy identified to this point. HD1 is much sufficient that its mild is estimated to be 13.5 billion years previous, or simply 300 million years after the Huge Big Bang. That makes it 100 million years older than the earlier record-setter, GN-z11, and suggests it might need among the very first (Inhabitants III) stars that emerged within the reionization following the universe’s “darkish ages.”
The workforce noticed HD1 utilizing about 1,200 hours of observations between the Spitzer House Telescope, Subaru Telescope, UK Infrared Telescope and VISTA Telescope. They verified the gap utilizing the Atacama Massive Millimeter/submillimeter Array, and the crimson hue was indicative of the intense redshift you’d anticipate from a really distant galaxy.
Astronomers nonetheless need to double-check their outcomes. The sign from HD1 has a 99.9 % significance, however observers will not make certain till they’ve a significance of 99.999 % or higher. The researchers might get that chance when the James Webb House Telescope takes a take a look at the galaxy utilizing its infrared-focused sensors.
If scientists can affirm HD1’s existence, that may elevate quite a few questions. HD1 does not match simply into current fashions of galaxy formation, and suggests there have been already extraordinarily shiny objects within the early universe. Not that the astronomy neighborhood would thoughts — this could assist refine their cosmological fashions.
This news was originally published by News VEX.