Increased level of atmospheric CO2 play an important role on crop growth and development. Elevated level of CO2 is not a stress factor for crops and plants because there is no CO2 sensor has been discovered in crops and plants.

In terrestrial C3 plants increased level of atmospheric CO2 accelerate the photosynthetic rate. Increased level of CO2 enhances the plant biomass. Hence, at the elevated level of atmospheric CO2, variability is observed on photosynthetic rate in plants and crops.
It is observed that long term contact to CO2 decrease the early inspiration of photosynthesis in plants and crops and often decrease the photosynthetic rate. Elevated level of CO2 results in the decrease of photosynthesis and involved in the fall of leaves in many species such as tobacco.
It is also observed that N and Rubisco content of leaf has been decrease after decrease in photosynthesis at the elevated level of CO2 in crops and plants. Normally, fall in leaves also found in many species for example in rice and wheat. Plants growth rate accelerate at the elevated level of CO2. It is also observed that stomata going to close at the restricted pressure of CO2.
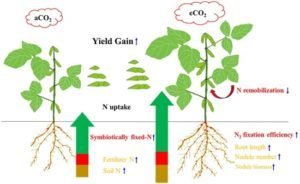
At the enhanced level of CO2, stored carbohydrates found in crops and plant species. Enhanced level of CO2 increases the root storage biomass in many plant species such as radish. The distribution of N to root and leaves has been enhanced at the increased level of CO2 exposure to plants and crops. There is redistribution of N content left from leaf surface to the sheath of leaf and roots at the elevated level of CO2 concentration.
In tobacco and radish, enhanced level of CO2 involved in the motivation of the growth and development of all the crops and plants. In other words, the rate of development of Triticum aestivum and Oryza sativa is not influenced at the higher level of carbon dioxide. The response of woody roots of plants is smaller at increased level of carbon dioxide.
At the elevated level of carbon dioxide, no major influence was observed shoot to root ratio in Liriodendron tulipifera, Quercus alba, Betul pendula, Pinus taeda, Pinus ponderosa or Fraxinus excelsior, Quercus petraea and Pinus sylestris.

Almost 56 % mass of the shoot has been recorded to be increased at the enhanced level of carbon dioxide after contact. It is also recorded that flowering of the plants cannot be influenced at the increased level of carbon dioxide while the creation of seeds enhanced 51 %. The content of soluble sugar not influenced at the higher level of carbon dioxide whereas the content of starch of stem enhanced in crops and plants.
In Arabidopsis thaliana, enhanced level of carbon dioxide increases the starch content which lower the nitrogen content in return, in many species. It is also found that at the higher level of carbon dioxide, the comparative growth is only for some extent while it promotes the health of Arabidopsis thaliana.
It is also found that elevated level of carbon dioxide accelerates the reproductive rate. In other words, increased atmospheric carbon dioxide has a major influence on environment, influence developmental processes and yield of plants and crops.
It is also recorded that enhanced level of carbon dioxide affect water use efficiency, enhance photosynthetic rate, increase the contents of carbohydrates and change the morphology of plants and crops. Effective level of carbon dioxide also changes the life span of many species.
In the duration of rate of vegetative growth, the rate of comparative growth is also accelerated at the enhanced level of carbon dioxide. The contact of carbon dioxide is takes place after the onset of seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. When carbon dioxide level became increased then it results in the production of plant growth regulators and the level of PGR is increases.
Elevated level of carbon dioxide is an environmental process which alter the function of genes in crops and plants. It is also observed that at the higher level of carbon dioxide the concentration of starch is also higher as compare to the normal concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
The elevated level of carbon dioxide the sugar content was not influenced in many species of plants and crops. Elevated level of carbon dioxide alters the wideness of leaves and the geometry of plants and crops. It is noted that 14 % seeds per silique and 33 % number of siliques per plant were higher at the increased level of carbon dioxide in plants and crops.
At the elevated level of carbon dioxide, the reproductive rate meaning is the whole number of seeds in the plants and crops. It is observed that dry weight of seeds scarcely influenced at the higher level of carbon dioxide. When plants are contacted to the higher level of carbon dioxide, the leaf area index is enhanced.
And this condition was observed from starting days after the application of carbon dioxide. When Arabidopsis thaliana is exposed to the increased level of carbon dioxide then the shoot biomass production become higher.
At last 38 % fresh shoot weight was observed as compare to the normal concentration of carbon dioxide. Thus, better yield of crops can be obtained in elevated CO2 atmosphere by better management practices.