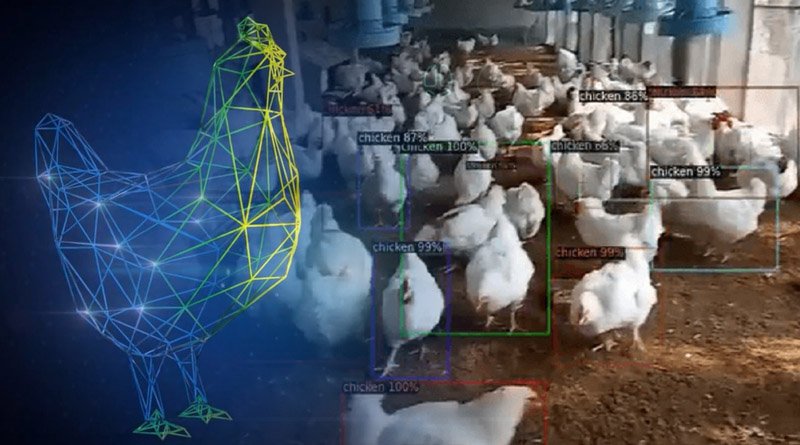
The poultry industry is a vital component of the global food supply chain, providing a significant source of protein for millions of people worldwide.
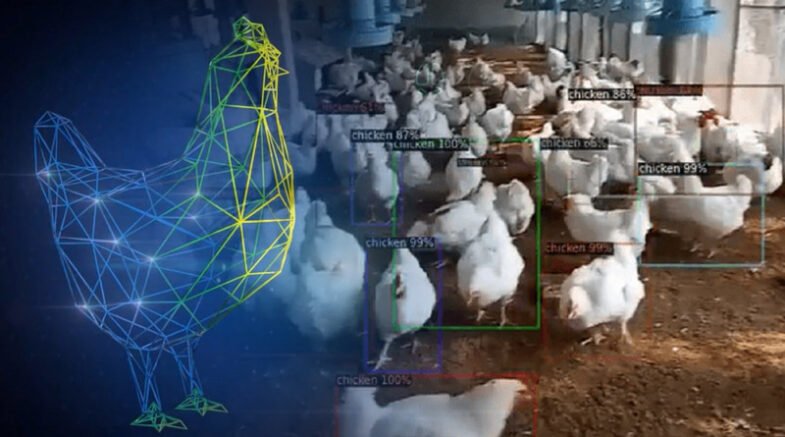

The article explores the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in poultry farming, including its applications, benefits, and challenges. AI can be used to automate monitoring systems, analyze data, and automate equipment and processes, resulting in improved productivity, enhanced animal welfare, and reduced environmental impact.
However, challenges such as cost, data privacy and security, and technical expertise must be addressed to ensure the effective implementation of AI in the industry. As the technology becomes more accessible, farmers must weigh the benefits and challenges of AI to make informed decisions about its use in their operations.
The poultry industry is a vital component of the global food supply chain, providing a significant source of protein for millions of people worldwide. With the growing demand for poultry products, farmers and producers are looking to leverage artificial intelligence (AI) to improve production efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance animal welfare.
In this article, we will explore the use of AI in poultry farming, including its applications, benefits, and challenges. Applications of AI in Poultry Farming:
Automated Monitoring:
One of the most significant applications of AI in poultry farming is the automation of monitoring systems. Sensors can be used to monitor the birds’ behavior, health, and welfare, providing farmers with real-time data on their flock’s condition.
For example, sensors can detect changes in the birds’ temperature, humidity, and air quality, alerting farmers to potential health issues before they become a problem.
This technology can also be used to monitor feed consumption, egg production, and even the growth rate of the birds, providing valuable insights into the productivity of the flock.
Predictive Analytics:
AI can also be used to analyze data collected from sensors and other monitoring systems, providing farmers with predictive analytics that can help them make more informed decisions.
For example, AI can analyze data on feed consumption, egg production, and the birds’ growth rate to predict when they will be ready for slaughter. This information can be used to optimize feed rations, reduce waste, and improve overall production efficiency.
Precision Livestock Farming:
Precision livestock farming (PLF) is an emerging field that uses advanced technologies like AI to monitor and manage livestock on a highly granular level. In poultry farming, PLF can be used to monitor individual birds, track their movements, and even identify specific health issues.
For example, AI-powered cameras can be used to monitor the birds’ movements and behavior, identifying potential signs of stress, injury, or disease. This technology can help farmers identify and treat health issues early, reducing the need for antibiotics and other medications.
Autonomous Equipment:
AI can also be used to automate equipment and processes in poultry farming, reducing labor costs and improving efficiency. For example, autonomous drones can be used to monitor the flock, collect data, and even deliver feed and water. Automated feeders and waterers can also be used to ensure that the birds have access to food and water at all times, without the need for constant human supervision.
Benefits of AI in Poultry Farming:
Improved Productivity:
One of the primary benefits of AI in poultry farming is improved productivity. By automating monitoring systems, analyzing data, and using predictive analytics, farmers can optimize their operations, reduce waste, and increase overall production efficiency. This can result in higher yields, lower costs, and increased profits for farmers and producers.
Enhanced Animal Welfare:
AI can also help improve animal welfare in poultry farming. By monitoring individual birds and identifying potential health issues early, farmers can provide timely medical treatment, reducing the need for antibiotics and other medications. This can lead to healthier birds, better living conditions, and improved animal welfare.
Reduced Environmental Impact:
AI can also help reduce the environmental impact of poultry farming. By optimizing feed rations, reducing waste, and improving production efficiency, farmers can reduce their carbon footprint and minimize their impact on the environment.
Additionally, by reducing the need for antibiotics and other medications, farmers can help prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which can have a significant impact on human health.
Challenges of AI in Poultry Farming:
Cost:
One of the primary challenges of AI in poultry farming is the cost of implementing the technology. AI-powered monitoring systems, equipment, and processes can be expensive, and many small-scale farmers may not be able to afford them. This can create an uneven playing field in the industry, with larger producers having a competitive advantage over smaller ones.
Data Privacy and Security:
Another challenge of AI in poultry farming is data privacy and security. Collecting and storing large amounts of data on the birds’ health, behavior, and other information can pose a risk to farmers if the data falls into the wrong hands. Farmers must ensure that their data collection and storage practices are secure and comply with data privacy regulations.
Technical Expertise:
Implementing AI in poultry farming requires technical expertise and knowledge. Farmers must have the skills to install and maintain monitoring systems, analyze data, and use predictive analytics to optimize their operations. Smaller-scale farmers may not have the resources or expertise to implement AI effectively, limiting their ability to compete in the industry.
Conclusion:
The use of AI in poultry farming has the potential to revolutionize the industry, improving productivity, enhancing animal welfare, and reducing the environmental impact of production. However, there are also challenges to implementing AI, including cost, data privacy and security, and technical expertise.
As the technology becomes more widespread and accessible, it will be important for farmers to consider the benefits and challenges of AI in their operations and make informed decisions about its use.

This article is jointly authored by Abdul Samad, Muhammad Hamza From Department of Poultry Science, Faculty of Veterinary and Animal Sciences MNS university of Agriculture Multan Pakistan.