The study conducted by researchers from the University of Cambridge, found that the use of pesticides and fertilizers is leading to a decline in the availability of food and habitat for birds.
A new study published in the journal PNAS has found that farmland practices are driving bird population decline across Europe. The study, which was conducted by researchers from the University of Cambridge, found that the use of pesticides and fertilizers is leading to a decline in the availability of food and habitat for birds.
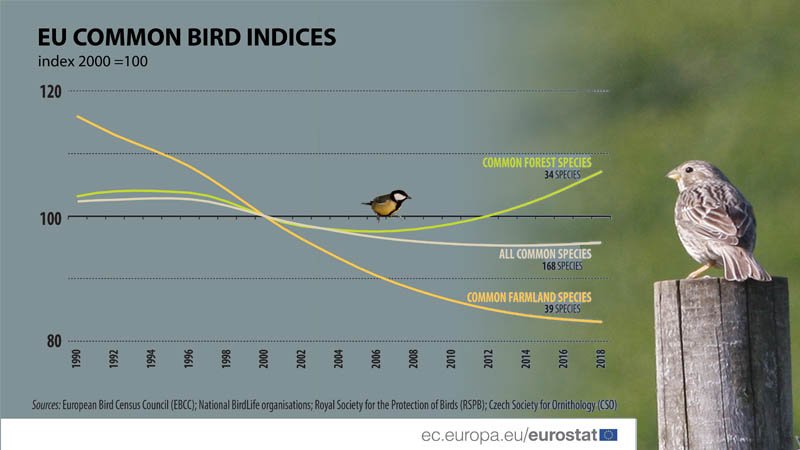
The study looked at data on bird populations from 1980 to 2015. The researchers found that the number of bird species in Europe has declined by an average of 13 percent over this period. The decline was most pronounced in farmland birds, which have declined by an average of 25 percent.
Commenting on the study Dr. Mark Avery, Chief Executive of the Campaign to Protect Rural England said, “This study is a damning indictment of the impact of modern farming practices on our birds. It is clear that we need to fundamentally change the way we farm if we are to prevent further declines in bird populations. This means reducing our reliance on pesticides and fertilisers, and creating more diverse and wildlife-friendly landscapes.”
The researchers found that the use of pesticides and fertilizers was the main driver of the decline in bird populations. Pesticides can kill birds directly, and they can also reduce the availability of food for birds by killing insects. Fertilizers can also reduce the availability of food for birds by increasing the growth of plants that birds do not eat.
“This study provides the most comprehensive evidence to date of the impact of agricultural intensification on bird populations across Europe. It is clear that intensification, as measured by the high use of pesticides and fertilisers, is the main driver of bird population declines, especially for those that feed on invertebrates. This is a major wake-up call for the farming industry and for policymakers”, said by Dr. Richard Thomas, Director of Science at the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds.
He further added, “We need to urgently reduce our reliance on pesticides and fertilisers if we are to halt the decline of our birds.”
Another recent study by the European Environment Agency found that between 1980 and 2010, the number of bird species in Europe declined by 18 percent. This decline is being driven by a number of factors, including:
Habitat loss and fragmentation
As human populations grow, more and more land is being converted to urban and agricultural use. This loss of habitat is a major threat to birds, as it reduces their food sources, nesting sites, and breeding areas.
Climate change
Climate change is also having a negative impact on bird populations. As temperatures rise, birds are being forced to move to new areas in search of food and suitable habitat. This can be a difficult and stressful process, and many birds do not survive the journey.
Pollution
Pollution from agriculture, industry, and transport is also harming bird populations. Pesticides and fertilizers can contaminate food sources, and air pollution can damage birds’ respiratory systems.
Overhunting
Hunting is still a major threat to bird populations in some parts of Europe. While hunting is regulated in most countries, illegal hunting still occurs.
The both studies’ findings suggest that there is a need for farmers to adopt more sustainable practices in order to protect bird populations. Farmers can reduce their use of pesticides and fertilizers by using integrated pest management (IPM) practices. IPM is a pest control strategy that uses a combination of methods, such as crop rotation, biological control, and mechanical control, to reduce the need for pesticides.
Farmers can also create more habitat for birds by planting hedgerows, leaving small areas of uncultivated land, and providing water sources for birds. By taking these steps, farmers can help to protect bird populations and ensure that they continue to play an important role in European ecosystems.
The decline of bird populations is a serious problem that has far-reaching consequences. Birds play an important role in ecosystems, and their loss can lead to a cascade of effects. For example, birds help to control insect populations, which can lead to an increase in pests. They also help to pollinate plants, which is essential for food production.
To address the decline of bird population, governments and conservation organizations can protect and restore habitats by creating new nature reserves, managing existing habitats, and reducing pollution.
Farmers can adopt more sustainable agricultural practices that reduce the use of pesticides and fertilizers, and create more wildlife-friendly habitats on their land, such as hedgerows and ponds. The public can be educated about the importance of birds and the threats they face, which can help raise awareness of the problem and encourage people to take action to protect birds.
The decline of bird populations is a serious problem, but it is not insurmountable. By working together, we can protect birds and ensure that they thrive for generations to come.