The group of diseases that involve abnormal cell growth with the potential to spread other parts of the body is called cancer. There are several types of cancer such as breast cancer, lung cancer and colorectal cancer etc.

The type of cancer that affects colon or rectum region is known as colorectal cancer also named as bowel cancer, rectal cancer or colon cancer. It occurs when some of the cells that line the colon or rectum grow abnormally and create a tumor.
According to American Cancer Society, about 1 in 23 women and 1 in 21 man develops colorectal cancer during their lifetime in United States. It is the leading cause of death in men and women.
With the use of advanced screening techniques and treatments, the mortality rate is falling. It may be benign, or malignant. A malignant cancer can spread to other parts of the body and damage them.
- Symptoms

- Risk factors
Risk factors include:
- older age
- High animal protein and saturated fat consumption
- Low fiber diet
- Alcohol consumption
- History of ovarian, uterine and breast cancer
- Family history
- Obesity
- Previous exposure of ulcerative colitis, Crohns disease or irritable bowel disease(IBD)
- Smoking
- Lack of physical activity
- Presence of polyps in the colon or rectum
Mostly colon cancers develop within polyps (adenoma). People with a tumor suppressor gene known as Sprouty2, are at higher risk of some colorectal cancers.
According to WHO (World Health Organization), after lung cancer, colorectal cancer is the second most common tumor among men and women. About 2% of people aged above 50 years can develop colorectal cancer in Western Europe.

- Stages of Disease
There are 5 (0-4) stages of colorectal cancer which gives the information of disease spread and helps to chose appropriate treatment.
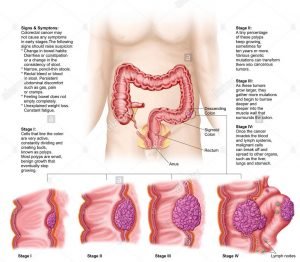
Recurrent: After treatment, disease can develop again and affect the rectum, colon or another part of the body.
At last stage of disease, Surgery is the best option.
- Diagnosis
Polyps are detected by the screening tests before they become cancerous, early stage diagnosis increases the chance of cure.
- Fecal occult blood test (blood stool test)
This test is not 100% accurate because blood loss may also occur in many other conditions, such as hemorrhoids. So it can give false results.
- Stool DNA test
In this test several DNA markers are analyzed that cancerous or precancerous cells shed into the stool. It is more accurate for the detection of colon cancer than polyps but cannot detect all DNA mutations.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy
A sigmoidoscopy only detects polyps or cancer in the end third of the colon and the rectum. It cannot detect a problem in any other part of the digestive tract.
- Barium enema X-ray
Barium is placed into the patient’s bowel as contrast dye in an enema form and is detected through an X-ray. Air is also added in a double-contrast barium enema. Barium coats the lining of bowel which provides clear image large intestine and a small portion of small intestine.
- Colonoscopy
The doctor examines the whole colon and rectum. Any polyps observed during this examination, are removed during this procedure. Sometimes tissue samples or biopsies are also taken.
- CT Colonography
A CT machine takes image of clear colon. If any abnormality is found then conventional colonoscopy may be recommended.
- Imaging scans
Ultrasound or MI scan can help to detect cancer when it spreads to other parts of the body.
- Treatment
Treatment depends on several factors, including size, location and stage of the cancer. Treatments may be radiotherapy, chemotherapy and surgery.
- Surgery for colorectal cancer
To reduce the risk of cancer spread, malignant tumors and nearby lymph nodes are removed through surgery. The bowel is sewn back together, in some cases rectum is compeletely removed. A colostomy bag is attached for drainage.
- Chemotherapy
In this procedure a machine or chemical is used to destroy the cancerous cells. Targeted therapy specifically targets the proteins that encourage the development of some cancers. Drugs that are used for colorectal cancer include bevacizumab (Avastin) and ramucirumab (Cyramza).
- Radiography
High energy radiations are used to destroy the cancer cells and to prevent them from multiplying. After surgery, both therapies are used to decrease the chances of recurrence.
- Ablation
By using radio frequency, ethanol or cryosurgery, the tumor is destroyed without removing.
- Recovery
Patient’s recovery depends on:
- Stage of disease at the time of diagnosis
- Colon area affected with cancer
- Health status of patient
Prevention
Lifestyle measure may reduce the risk of developing colorectal cancer:
- Regular screenings: people of older age, A family history of this type of cancer and crohns patients should have regular screenings.
- Nutrition: A diet with plenty of fiber, fruit, vegetables, good quality carbohydrates, a minimum of red and processed meats reduces the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Exercise: Moderate, regular exercise has been shown to have a significant impact on lowering a person’s risk of developing colorectal cancer.
- Body weight: Being overweight or obese raises the risk of many cancers such as colorectal cancer.
Authors: Lubna Majeed, M. Naeem Faisal, Alishbah roobi, Noreen Aslam, Samia Ali
Institute of Pharmacy, Physiology and Pharmacology, University of Agriculture Faisalabad, Pakistan
Corresponding Author: lubna.majeed384@gmail.com