Earth climate is changing day by day faster than any point of the history of modern civilization, primarily as a result of human activities.

Global climate change has already resulted in a wide range of impacts throughout the every region of every country and many sectors of the economy that are expected to grow in coming years.
The earth climate has changed throughout the history. Just in last 650,000 years there are seven cycles of glacial advance with the sudden change of the last ice age of about 7,000 years ago making the beginning of modern climate change era and present human civilization.
Most of these climate changes are due to very small variations in the atmosphere the amount of solar energy our planet receives. The current warming climate trend is very important because most of the result of human activities since mid-20th century.
Satellites and other technical advances has enabled scientist to collect many types of information about earth planet and its climate on global scale. The collected data shows the change in temperature in other words change in climate.
Many gases have heat trapping nature like Carbon dioxide, Methane, Nitrous Dioxide and fluorinated gas. Their contribution is shown in below graph.
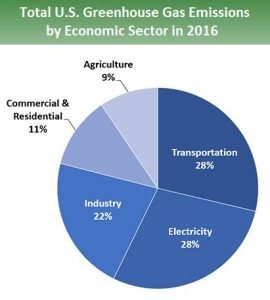
These gases play very important role in trapping heat waves mostly infrared waves that cause the increase in atmospheric temperature. These gases are called as greenhouse gases. Vehicles, refrigerators, agriculture sector, industries and electricity generation plants are major sources of these greenhouse gases.
The ice melting from Greenland, Antarctica and Tropical Mountain glaciers show that the earth climate respond to changes in greenhouse gas levels. Ancient evidence can also be found in tree rings, ocean sediments, coral reefs and layers of sedimentary rocks. The ancient evidence shows that the current warming is occurring roughly ten times faster than the average rate of ice-age recovery warming.
The Evidence for Rapid Climate change
- Global Temperature Rise
The Earth surface temperature has risen about 1.62 degree Fahrenheit (0.9 degree Celsius) since the late 19th century. This change is driven due to increase in carbon dioxide and other humane made emissions into atmosphere.
Most of the rise in temperature occurred in last 35 years with five warmest years on the record since 2010. Year 2016 is recorded as the warmest year with the 8 warmest months from January to September than the previous years. The warmest month on the Scale that was recorded was June 2016.
- Warming Oceans
The oceans are absorbing most of heat radiated from sun. The oceans top 700 m (about 2300 ft) of ocean showing warming of more than 0.4 degrees Fahrenheit since 1969.
- Shrinking Ice Sheets
The Greenland, Antarctic ice and Glaciers sheets are decreasing day by day. Gravity recovery and Climate experiment show the Greenland lost an average of 281 billion tons of ice per year between 1933 and 2016. While Antarctica lost about 119 billion tons during the 1933 to 2016. Antarctica ice mass loss has tripled in last decades.
- Glacial Retreat
Glaciers are retreating everywhere across the word including in the Alps, Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, Alaska and Africa.
- Decreased Snow Cover
Satellite observations shows that the amount of spring snow cover in Northern hemisphere has decreased over the last 50 years and that snow is melting continuously.
- Sea level Rise
Global sea level has risen about 8 inches (20 cm) in the last 100 years. The rate in the last twenty years is nearly double that of the last century and is increasing slightly every year.
- Declining Arctic Sea Ice
From the last several years the extent and thickness of Arctic sea has decreased.
- Extreme Events
The number of high record temperature event in the world has been increasing while the number of low temperature records has been declining since 1950. The number of intense rainfall is increasing.
Due to industrial revolution the soil and oceans acidification is increasing. The surface acidity of oceans has increased by 30%. This increase is due to humans emitting more carbon dioxide into atmosphere and more being absorbed by oceans. About 2 million tons per years carbon dioxide absorption is increasing into the upper most layers of Oceans.
Effects of Climate Change
Increase in temperature simultaneously will cause expanding of oceans, ice melting in Antarctic and Greenland will also contribute to the sea level. By 2100 sea level could rise by 25 to 50 cm.
High sea levels will threaten the low laying coastal areas of Bangladesh and Netherland, millions of areas of land will be at danger from flooding. It will cause people to leave their houses.
Low laying areas of cities will be mostly affected by rising sea. Changing weather condition will alter the crops sowing and harvesting time. High Temperature will affect the crops of cooler climate like sugarcane and maize.
Changing rainfall pattern will alter the crop season to grow. This climate change will affect the countries having not enough food. Brazil, some parts of Africa, South East Asia and China will be affected the most and many people could face the Starvation.
Across the world there is a huge demand for water in many regions, such as central and eastern Africa there is less water for human consumption as well as for field crops. Changes in climate will cause less rainfall in some countries and more in others.
It may be the drier areas will become drier and wet areas will become more wet by receiving more rainfall. Daily weather and daily temperature will change due to climate change. All living activities will be disturbed.
Animals like polar bear and seals will mostly affected by climate change, they will have to find new hunting areas and habitat. These species will become extinct due high temperatures because they are native to low temperatures.
Climate change will affect every life but some populations will have more risk of being victim. Countries such as China, Egypt have large populations on their coastal areas they have to move away from coastal areas to avoid flood losses. The effect on people will depend on how well native populations can adapt to the changing environment.