The heart and kidney are like a married couple, if one isn’t happy the other one isn’t either.”Dr. Luke Laffin
Author: Anoosh Fatima
Introduction
Kidneys are two bean-shaped organs found on either side of the abdomen tasked with filtering blood from all toxins and other waste materials along with maintaining the homeostasis of the body. Due to the pressure-sensitive nature of the mechanisms involved, hypertensive patients are more inclined towards kidney failure. This essay sheds light on how the two are related and also the red flags hypertensive patients need to keep a lookout for.
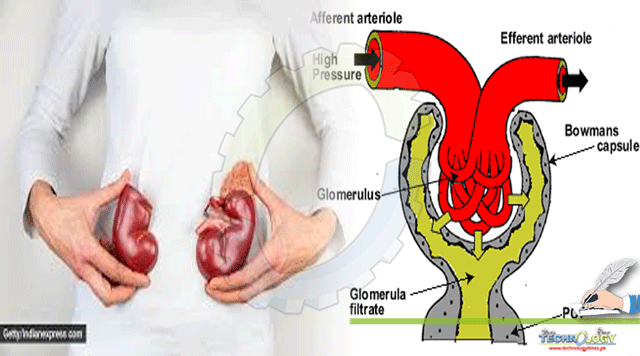
Ultrafiltration
The efficiency of a kidney is analyzed using a parameter known as Glomerular Filtration rate (GFR), which is estimated to be less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 in a healthy adult (Pugh, 2019). Another marker for deteriorating kidney health is presence of proteinuria i.e. proteins in urine.
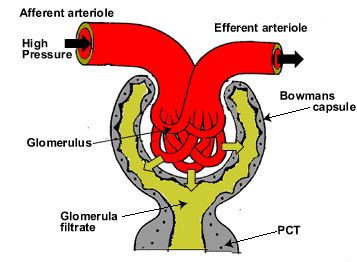
Kidneys carry out filtration in two ways i.e. ultrafiltration and reabsorption. Ultrafiltration employs the principle of pressure difference, where the artery entering the glomerulus (a mesh of capillaries) has a thicker lumen as compared to the one leaving it. These are called afferent and efferent arterioles, respectively. This pressure difference facilitate particles to leak or “filter” out of blood and into the kidney, a process known as ultrafiltration. Thus, a suitable pressure is required for kidneys to function efficiently. There are specialized cells present near the afferent arteriole to sense and maintain it.
Early Diagnosis
The failure to attain ideal blood pressure (BP) reductions may be contributing to the continuing rise in the incidence of end-stage renal disease in patients. This is why people with prolonged hypertension or heart failure are at a greater risk of developing kidney failure and are encouraged to regularly test for various potential symptoms of kidney failure. These tests are:
1. Regular blood pressure check
As hypertension is becoming more and more prevalent in the population, the use of BP apparatus has exponentially increased too and the device can be found in every other household. Despite it being a healthy practice to regularly monitor BP, every once in a while, 24-Hour ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM) should also be incorporated in the routine as research has proven it give a more accurate analysis of BP and cardiovascular health. The accepted range for optimum readings given by American College of Cardiology (ACC) are 135/85 mmHg during the day and 120/70 mmHg at night.
2. Protein-to-creatinine test for proteinuria
An analysis of urine can point towards a pandora of health issues, one such is levels of proteins in the urine that indicate decreasing muscle mass, which points towards the kidneys not being able to filter out the blood effectively, thereby allowing larger particles like proteins through. Protein-to-creatinine ratio, taken from a spot urine sample, is one of the most common methods, but occasionally albumin-to-creatinine ratio method is also employed for a more precise detection (Pugh, 2019). If the problem persists, the healthcare practitioner may recommend a kidney ultrasound.
A common myth is that a high water intake would treat proteinuria, although undoubtedly a good water intake is crucial for kidney health, but in this case it will only dilute urine, depicting a lower level of protein in the results. This is not to be mistaken as an improved kidney health as the damage still persists.
Conclusion
The adverse effects of high BP on renal health are evident from the text above. It is irrelevant if the kidneys are functioning naturally on their own or with the aid of some artificial procedure like dialysis, as the risk persists in both. So, it is extremely crucial to maintain a healthy BP by embracing a lifestyle with adequate physical exercise and a balanced diet. Regular visits to the healthcare practitioner hold equal importance so that the most suitable medicine is prescribed according to the current health status.
References
- Pugh, D., Gallacher, P.J. & Dhaun, N. (2019). Management of Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease. Drugs 79, 365–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-019-1064-1
- Morgan, S. (2011, July 8). Water Intake & Kidney Damage. LIVESTRONG.COM. https://www.livestrong.com/article/403583-water-intake-kidney-damage/
Author Bio: Anoosh Fatima is a Biomedical engineering student who enjoys writing on topics ranging from science and technology to history and literature and is welcome to learning new things!