The ambitious foray into artificial rain by Pakistan holds a beacon of hope for the nation’s air quality, particularly in regions grappling with the debilitating effects of smog.
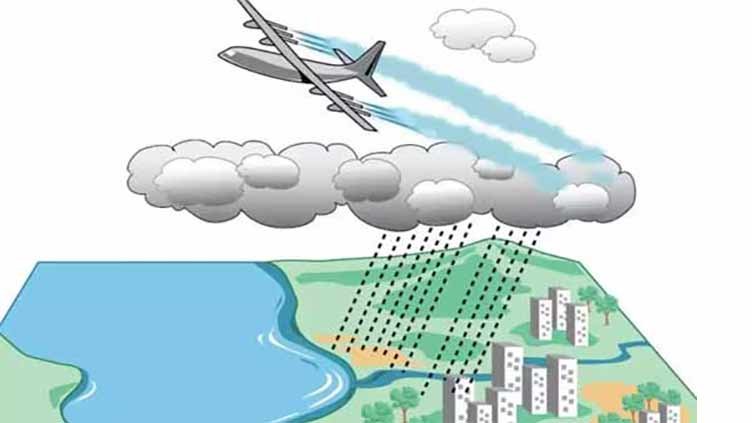
Pakistan is gearing up for an innovative experiment to combat the smog crisis plaguing its skies. The plan involves harnessing the power of artificial rain, a technique employed by various nations worldwide to address environmental challenges. This ambitious endeavor is spearheaded by a team from Punjab University’s Centre for Integrated Mountain Research, under the guidance of Professor Munawar Sabir.
The Experiment Unveiled
Scheduled to kick off in the Khanspur mountainous region, where humidity and cloud cover prevail, the experiment aims to alleviate the smog predicament. Following this initial phase, the team plans to extend its reach to Lahore, one of the most polluted cities globally, after November 19, 2022. The technique involves the strategic spraying of salt over clouds, enhancing their density and water content, ultimately triggering rainfall.
Benefits of Artificial Rain
Clearing the Smog: A Beacon of Hope for Air Quality
The ambitious foray into artificial rain by Pakistan holds a beacon of hope for the nation’s air quality, particularly in regions grappling with the debilitating effects of smog. As a lethal amalgamation of smoke and fog, smog crisis has become a ubiquitous challenge in many urban landscapes, impacting not only the health of citizens but also diminishing the visibility to hazardous levels.
The experiment’s primary objective is to act as a mitigating force against the adverse effects of smog crisis. By inducing rainfall through the strategic application of salt over clouds, the team aspires to wash away the pollutants that contribute to the thick smog layers. This concerted effort aims to cleanse the atmosphere, providing relief to millions of people who endure respiratory issues and reduced quality of life due to prolonged exposure to smog.
Furthermore, the improved air quality resulting from artificial rain is anticipated to have cascading positive effects on public health. Respiratory conditions, exacerbated by smog crisis, may witness a decline, and the overall well-being of communities could experience a significant uplift.
Environmentally Targeted: Unleashing the Power Against Drought, Pollution, and Beyond
Artificial rain emerges as a versatile and potent tool on the global stage, not confined to Pakistan’s smog-choked skies alone. Its application extends far beyond the immediate objective of clearing pollutants, encompassing a range of environmental challenges.
Combatting Drought: Artificial rain has proven instrumental in addressing drought conditions, offering a lifeline to regions grappling with water scarcity. By inducing precipitation in arid landscapes, it becomes a powerful ally in replenishing water sources, supporting agriculture, and ensuring the sustenance of ecosystems.
Fighting Pollution: The use of artificial rain to combat pollution extends beyond smog. Many nations have leveraged this technique to cleanse the atmosphere of pollutants, both airborne and deposited on surfaces. The resultant rainfall acts as a natural purifier, washing away contaminants and contributing to overall environmental cleanliness.
Versatility in Environmental Challenges: What sets artificial rain apart is its adaptability. Whether facing the challenges of drought, combatting various forms of pollution, or seeking innovative solutions to other environmental crises, this technique offers a multifaceted approach. It aligns with a broader commitment to sustainable practices and environmental stewardship.
The Race Against Time
One pertinent question arises: How long until the experiment yields tangible results? While the timeline may vary based on multiple factors, from cloud conditions to the effectiveness of the applied method, initial observations are anticipated soon after the experiment’s commencement.
Risks and Considerations
Impact on Natural Rainfall Patterns: Navigating the Waters of Ecological Harmony
The introduction of artificial rain, while holding promise in addressing specific challenges, raises concerns about its potential impact on the delicate dance of natural rainfall patterns. The intricate balance of the water cycle, essential for ecosystems and agricultural sustainability, might face disruption.
As droplets form artificially and descend from the skies, questions arise about how this intervention might influence the timing, distribution, and overall rhythm of precipitation. The repercussions could extend beyond the immediate experiment site, affecting neighboring regions and upsetting the harmonious equilibrium that nature has meticulously crafted over millennia.
Environmental Consequences: Unraveling the Ecological Tapestry
In the pursuit of cleaner skies, the use of chemicals or particles to induce artificial rain introduces a layer of complexity to the environmental equation. While the immediate goal is to combat smog crisis and pollutants, there’s a discernible risk of unintended consequences.
The potential for environmental damage or contamination looms as a shadow over the experiment. The chemicals employed may interact with ecosystems in unpredictable ways, affecting flora, fauna, and even water sources.
The need for meticulous research and stringent safeguards is paramount to mitigate these potential adverse effects and ensure that the cure does not become a new environmental ailment.
Weather and Climate Implications: Unveiling the Unknowns of Atmospheric Manipulation
The alteration of precipitation patterns through artificial rain isn’t confined to the immediate vicinity; it extends its influence to the broader canvas of local weather and climate. As clouds are coaxed into releasing their water artificially, the intricate ballet of atmospheric dynamics may undergo shifts with far-reaching consequences.
Unforeseen outcomes, such as changes in temperature, wind patterns, or atmospheric pressure, could emerge. These alterations may ripple through the regional climate, introducing uncertainties that demand careful consideration.
The experiment, intended to alleviate one environmental challenge, inadvertently becomes a participant in shaping the broader climatic narrative, underscoring the importance of comprehensive climate studies and ongoing monitoring.
The Evolution of Artificial Rain Experiments in Pakistan
The concept of inducing artificial rain in Pakistan, particularly in response to environmental challenges such as heatwaves and smog, has a history marked by both ambition and skepticism. The journey unfolds through attempts, challenges, and the quest for innovative solutions.
Early Ventures: 2015 and the Heatwave
In 2015, facing an intense heatwave, the government of Pakistan explored the possibility of using cloud seeding technology to generate artificial rainfall in parts of Sindh. The ambitious project involved firing rockets propelled by sugar at the clouds, a strategy intended to increase their density and water content, thus triggering rainfall.
The proposed cost of approximately Rs 300 million underscored the scale and complexity of the endeavor, requiring collaboration with the Pakistan Army Aviation Division.
However, this proposal faced resistance from experts who raised valid concerns. The potential environmental repercussions, such as disrupting natural rainfall patterns and the water cycle, led to a reconsideration of the plan.
The unsuitable atmospheric conditions in Karachi, marked by high temperatures and low humidity and cloud cover, further fueled skepticism. Some experts advocated for a shift in focus towards improving water supply management and reducing greenhouse gas emissions as more sustainable alternatives.
The Emergence of a New Approach: 2021 and Beyond
Fast forward to 2021, and a new chapter unfolds in the form of a venture by a team from Punjab University’s Centre for Integrated Mountain Research, led by Professor Munawar Sabir.
The team aimed to counter smog crisis through artificial rain, testing the technology in the Khanspur mountainous area, known for its high humidity and cloud cover. Lahore, one of the world’s most polluted cities, became a focal point for the experiment after November 19, 2021.
The technique involved the strategic application of salt over clouds, a method intended to make them denser and heavier with water, ultimately leading to rainfall. The team, driven by its commitment to environmental improvement, utilized its own resources and equipment for the experiment, operating independently of official support or funding.
Challenges and Unanswered Questions: 2023 and Beyond
As of 2023, the outcome and impact of the artificial rain experiment in Lahore and other cities remain unclear. Reports suggest a revival of the project, indicating an ongoing pursuit of innovative solutions to environmental challenges. However, the lack of concrete evidence regarding the success or failure of the artificial rain raises questions about the viability and effectiveness of this approach.
Lessons Learned and Future Paths
The history of artificial rain experiments in Pakistan reflects a willingness to explore unconventional solutions to pressing environmental issues. Yet, it also underscores the importance of careful research, evaluation, and a nuanced understanding of the potential risks associated with such interventions.
As Pakistan navigates this uncharted territory, the lessons learned from both successes and challenges will shape the future path of environmental innovation in the region. The need for ongoing research, transparency, and collaboration emerges as essential elements in the pursuit of sustainable solutions.
The Global Landscape
While Pakistan joins the ranks of countries like China, India, Thailand, and Israel in experimenting with artificial rain, it is essential to recognize that this technique is not a panacea. Careful research, ongoing evaluation, and a commitment to minimizing environmental impacts are imperative before widespread implementation.
As Pakistan navigates the uncharted waters of artificial rain, the world watches with anticipation, recognizing the potential for innovative solutions to pressing environmental challenges. The journey towards cleaner skies and healthier communities is undoubtedly a complex one, but the pursuit of sustainable solutions is a step in the right direction.