Chinese researchers have created a mobile intelligent robotic computed tomography (CT) that can be very useful for patients who are in critical condition.

Chinese researchers have created a mobile intelligent robotic computed tomography (CT) that can be very useful for patients who are in critical condition.
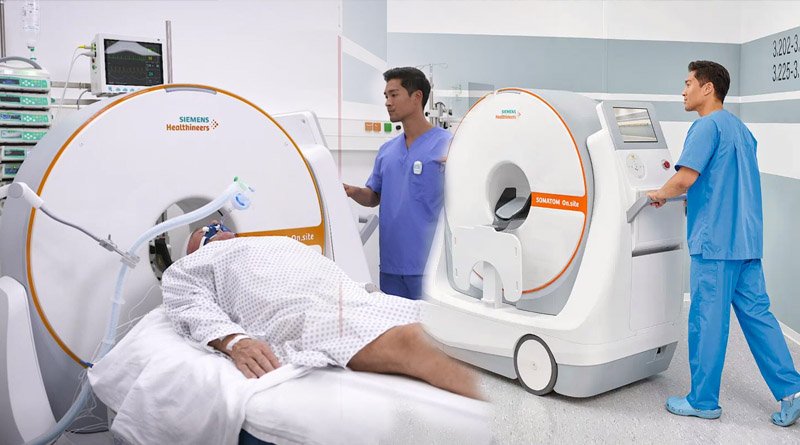
The robotic mobile CT is 135 cm tall and weighs 260 kg, in contrast to the usual bulky ones. At the Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, it has already undergone testing. It has low radiation and low energy requirements.
The device, which includes features like voice control, route planning, and automatic obstacle avoidance, was created by researchers from the hospital and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China over the course of ten years.
The device can be told to move directly to the patient’s bedside for examination and upload the results in real time, according to Xu Ruxiang, the research team’s chief expert. To push patients in critical condition to the computed tomography examination room in the past, however, it required three to four people, Xu added.
According to Xu, this mobile treatment model will greatly increase the effectiveness of disease examination and treatment, aid in the survival of more critically ill patients, and lessen the workload on medical staff.
The term “CT scan” is frequently used to refer to computed tomography. A CT scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that creates images of the inside of the body using a combination of X-rays and computer technology.
Any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, organs, and blood vessels, is shown in detail. Compared to traditional X-rays, CT scans are more detailed. A beam of energy is directed at the body part being studied in standard X-rays. After the energy beam passes through the skin, bone, muscle, and other tissues, it varies and is captured by a plate behind the body part.
The X-ray beam rotates in a circle around the body during a CT scan. This provides much more detail and enables numerous views of the same organ or structure.