During its 33rd low pass over the cloud tops of Jupiter on April 15, 2021, NASA’s Juno spacecraft captured the intriguing evolution of a feature in the giant planet’s atmosphere known as “Clyde’s Spot.”
The feature is informally named for amateur astronomer Clyde Foster of Centurion, South Africa, who discovered it in 2020 using his own 14-inch telescope.
On June 2, 2020, just two days after Foster’s initial discovery, Juno provided detailed observations of Clyde’s Spot (image below), which scientists determined was a plume of cloud material erupting above the top layers of the Jovian atmosphere just southeast of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot, which is currently about 1.3 times as wide as Earth.
These powerful convective outbreaks occasionally occur in this latitude band, known as the South Temperate Belt. The initial plume subsided quickly, and within a few weeks it was seen as a dark spot.
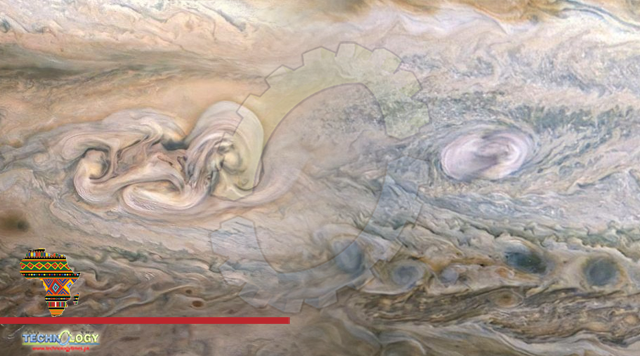
Many features in Jupiter’s highly dynamic atmosphere are short lived, but the April 2021 observation from the JunoCam instrument (top image) revealed that nearly one year after its discovery, the remnant of Clyde’s Spot had not only drifted away from the Great Red Spot but had also developed into a complex structure that scientists call a folded filamentary region.
This region is twice as big in latitude and three times as big in longitude as the original spot, and has the potential to persist for an extended period of time.
The lower image was taken on June 2, 2020, around 3:56 a.m. when the spacecraft was about 28,000 miles (45,000 kilometers) from Jupiter’s cloud tops.
The upper image was taken on April 15, 2021, at 4:58 p.m. PDT (7:58 p.m. EDT). At the time, the spacecraft was about 16,800 miles (27,000 kilometers) from Jupiter’s cloud tops, at a latitude of about 30 degrees South. Another citizen scientist, Kevin M. Gill, processed both images from raw JunoCam data.
Originally published at Sci tech daily