This article includes detailed information about the Fragile X Syndrome (FXS). Fragile X Syndrome is one of the most commonly found forms of inherited mental retardation. The individuals affected with this syndrome display a wide range of behavioral and developmental problems.

By Sarah Nauman and Zainab Asad
Abstract
In recent years, many advancements have been made to have an improved understanding of this syndrome and to possibly find its cure.
Thus, this article highlights the basic aspects of FSX and all the associated information to produce a better understanding of this syndrome.
-
Introduction
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic disorder that causes mental retardation. FXS is caused by the mutation in a gene that is present on the X gene which is known as Fragile X Mental Retardation-1 or FMR 1 gene. This gene is present in every cell of the body. The mutation in the FMR 1 gene is the molecular basis of the fragile X syndrome. The protein it makes is essential for normal brain development. In FXS the FMR 1 gene fails to produce the protein or makes very little of it. To understand type of mutation we first must know that there are four nucleotides Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine which are attached to each other by hydrogen bonds in a DNA molecule to form genes that encode proteins such as FMR1 gene. The beginning of the gene has a repetitive trinucleotide sequence of CGG, normally the number of CGG repeats lies in between 6 to 54 and if it is between 55 to 200 then there is a chance of mutation, but in most cases the brain develops normally. However, the count increases more than 200 when the gene is turned off, so there is mutation causing FXS.
FXS affects both males and females. However, females often have milder symptoms than males. The exact number of people who have FXS is unknown, but a review of research studies estimated that about 1 in 7,000 males about 1 in 11,000 females have been diagnosed with FXS.
-
Sign and symptoms
Signs and symptoms of a FXS are following
-
Developmental delays such as:
- Delay in sitting
- Delay in Walking
- Do not talk as other children of same age
-
Learning disability (trouble learning new skills)
-
Social and behavior problems such as:
- Not making eye contact
- Anxiety
- Trouble in paying attention
- Hand flapping
- Acting and speaking without thinking
- Being very active
-
Physical symptoms
- Long face
- Large jaw
- Long and prominent ears
- Macrocephaly (overly large head)
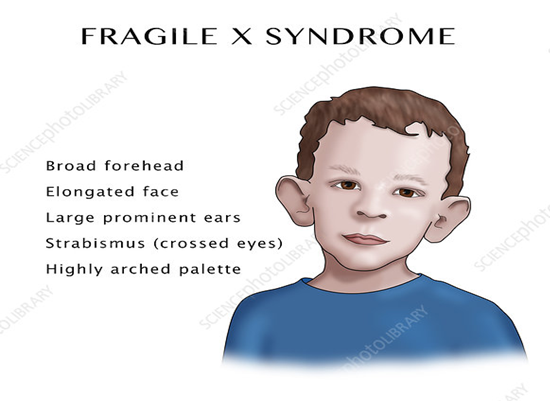
Figure 1 physical symptoms of FXS
-
Diagnosis
An individual affected with FRX can be diagnosed with the help of DNA testing. The chromosomes of the affected individuals or the people who may be at the risk of carrying the mutation, both can be determined by extensive examination of the CGG repeats on the FMR1 gene. Through different laboratory techniques the DNA fragments containing the repeated sequences of CGG, can be amplified and thus mutations can be identified.
The DNA testing of individuals having a family background of FXS or in fetuses, when the mother is a carrier of this syndrome is important to detect the possibility of mutation in the FMR1 gene.
Another way for the diagnosis of FXS can be done through population screening. That method involves studying the prevalence of traits occurring in a population and hence determining the presence of specific disorders in that population. The different phenotypes of FXS such as its characteristic trait that is mental retardation along with other behavioral and developmental problems can be observed and the individuals possessing such traits can be diagnosed.
-
Treatment
There is no medicine that can cure FXS. However, the individuals affected with FXS can be cured with self-help therapies.
These therapies can help to improve the behavior and individual capabilities. The behavior of individuals with FXS can be improved by
- Special type of education that enables them to overcome learning problems
- Language and behavioral therapies
- Some medicines can also be given to manage symptoms such as hyperactivity and many behavioral problems
As mentioned above there is no medicine that can cure FSX, however certain medications do exist for controlling some of the symptoms of FSX such as behavioral problems etc.
The individuals affected with FSX, should be given regular therapies to improve their behavior and social skills.
Moreover, genetic counselling of affected parents is also important so they can make informed decisions with respect to family planning.
-
How can it be managed?
It can be managed through early intervention services; Early intervention services help children from birth to 3 years old to learn important skills. These services may improve a child’s development. Even if the child has not been diagnosed with FXS, they may have the symptoms. Through this system, patients can ask for an evaluation. In addition, treatment for symptoms, such as speech therapy for language delays, often does not need to wait for a formal diagnosis. Early intervention is extremely important, treatment services at any age can be helpful. Having support and community resources can help increase confidence in managing FXS, enhance quality of life, and assist in meeting the needs of all family members. Some countries have created centers (such as the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, America) which are working for intervention and support and trying to find more about the mutation and how it can be cured.
References
|
1. |
center of disease control and prevention. fragile X syndrome. [Online].; 2020 [cited 2020 11 10. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/fxs/facts.html. |
|
2. |
WebMD. WebMD childern health medical reference. [Online].; 2020 [cited 2020 11 9. Available from: https://www.webmd.com/children/medical-reference/default.htm. |