The sufficient knowledge of antigen presentation of SARS-CoV-2 will be very helpful for COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Inopportunely, we do not have sufficient reports regarding the antigenic presentation of COVID-19.
By Maria Daud Bhatti*, Wafa Majeed, Muhammad Naeem Faisal, Mahnoor Syed, Nabeeha Shahab, and Hafsa Iqbal
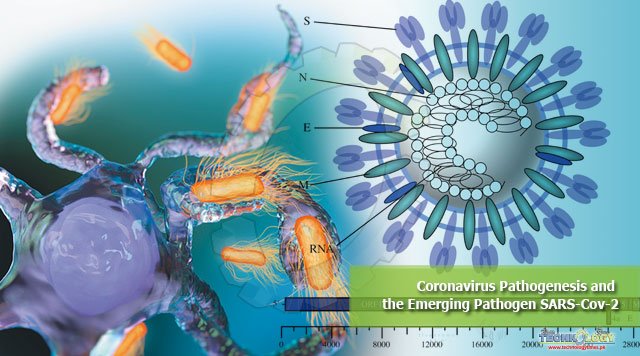
Corona viruses be the member of Orthocoronavirinae subfamily with the family Coronaviridae, Order Nidovirales. The genera of subfamily of Orthocoronavirinae, divided into four categories particularly α-coronavirus, β-coronavirus, γ-coronavirus and δ-Coronavirus.
The genetic make-up of CoV having a one-stranded ribonucleic acid within the proportion of 26kb and 32kb, the biggest genetic make-up of all well-known ribonucleic acid viruses. Both α and β-CoV are considered to cause diseases in vertebrates, while δ and γ-Coronavirus cause infection to feathered creature.
In the past, SARS-CoV (2003) transmitted the disease to 8098 personals across the world with mortality rate of 9%. On the other hand, coronavirus (Covid-19) caused infection 11.104M individuals with mortality rate of 4.74%, all over the world, as on July 4, 2020.
Due the genetic modification at spike protein in RBD portion of coronavirus may increase the rate of transmission.
Risk factors:
Notwithstanding the risk factors of COVID-19 are still opaque but many researches revealed the fact that patient having chronic illness or co-existing disorder or cancer or immune disorder are prone to infection. Due to these factors mortality rate in such person would be higher than normal patient.
The data of COVID-19 patient in hospital showed that about 50.5% of patients having a chronic illness from which 40.4%, were suffering from CVS and cerebrovascular diseases. In the company of 1099 patients revealed that 23.2% have coexisting diseases such as HTN (14.9%) and diabetes mellitus (7.4%).
However, these studies communicate various meaningful findings.
- Children, middle-aged adults and elderly people were most commonly infected by coronavirus.
- The frequency of infected men is higher than women.
- Doctors and health care worker and hospitalized patients can infect by this virus from the hospital.
- About 20% of coronavirus patients have underlying diseases and in severe patient have comorbidities disorder as compared to non-severe patients.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of COVID-19 is primarily consists of
- History of contact
- Clinical symptoms
- CT scan
- Chest CT
- Blood culture
- Virology investigation
- Immune identification technology (IgM/IgG, ELISA)
- Nucleic acid detection
- RT-qPCR
Pathogenesis:
1: Virus attachment and replication:
Spike protein of coronavirus has been reputed as a important parameter for entry into host cells. The wrapped S protein attached to host cell through their receptor such as ACE2 for COVID-19. The access of coronavirus into host cells was primarily known to be proficient by pointed membrane union between the cell membrane of host cell and virus.
The viral infectivity resulted from proteolytic cleavage of S protein (S20) that is conciliated by virus and membrane fusion. Moreover clathrin-idependent and dependent endocytosis may conciliate the virus entry.
Afterward, the virus gain entry into host cell and liberate its RNA into the cytoplasm then structural and poly-protein are being translated. After this replication of viral RNA begin.
The freshly formed wrapped spike glycoproteins were moved towards endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi apparatus which may lead to the formation of Nucleocapsid by the fusion of viral genome, and protein coat.
Then, finally virus containing vesicle from Golgi bodies and ER started fusion with membrane to liberate the newly-formed viruses.
2: Antigen demonstration:
While the virus gain entry into host cells, its antigen will be delivered to the antigen presenting cells (APC), which is a cardinal role of immunity against viral diseases. Antigen is conferred by major histocompatibility complex (HLA or MHC in humans) and later on identify by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (virus specific).
Therefore, the sufficient knowledge of antigen presentation of SARS-CoV-2 will be very helpful for COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Inopportunely, we do not have sufficient reports regarding the antigenic presentation of COVID-19.
However, we collect some data from the former researches and concluded that MHC I and MHC II are major contributor for antigenic presentation of COVID-19.
3: Anti-body mediated immunity:
After antigenic appearance antibody mediated immunity may stimulated, which negotiate the peculiar T and B cells. Alike to usual viral diseases, SARS-CoV-2 has an ordinary style of IgM and IgG antibodies presentation against coronavirus.
The IgM antibodies which are SARS-specific will start disappearing at the 12 of week while the SARS-specific IgG antibodies stay longer in the body which may be the evident of protective function and IgG antibodies against COVID-19 chiefly are N-specific or S-specific antibodies.
In comparison to antibody mediated immunity there are much more researches on cell mediated immunity against coronavirus. The latest researches reveals that there are massive reduction in the number of CD4þ and CD8þ T cells in the venous blood of COVID-19 patients as its condition is extremely energizing as certify by high percentage of CD4 (3.47%) and CD8 (39.4%).
In the same way, acute stage reaction in patients with coronavirus is related with critical reduction of CD4 and CD8 T-cells. In coronavirus recovered patient CD4 and CD8 memory T-cells can persists till 3-4 years even if there is no antigen and can accomplish T-cell expansion and formation of interferon gamma.
Even after Six years patient infected with coronavirus still have specific memory T-cells in 14-23 recovered patients. These judgments may allow fruitful information for designing vaccine against coronavirus.
4: Cytokine fight in SARS-CoV-2:
In SARS-CoV-2-infected patients who were admitted in the hospital 14.6% died in the early stages of the outburst due to non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema is the ordinary immunological stage for SARS-CoV-2 infections.
One of the principal medium for acute respiratory distress syndrome is the cytokines assault. A large number of chemokine (CCL-2, CCL-3, CCL-5, CXCL-8, CXCL-9, and CXCL-10) and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α,TGF-β, IL-1b, IL-6, IL-12, IL-18, and IL-33 ETT will be released by the immune effectors cells in COVID-19 infected patient. That results in rampant intrinsic inflammatory feedback.
Alike studies on SARS-CoV, and severe MERS-Cov infected patients exhibit increased level of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IFN-α) and chemokine (CCL-5, CXCL-8, CXCL-10 ) as compared to the patient having mild to moderate disorder.
The cytokine assault will provoke a furious strike to the body by the immune system and may lead to death in critical patients due to multiple organ failure or acute respiratory distress syndrome.
5: Coronavirus immune evasion:
SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV use diverse actions to avert immune responses for their survival in host cells. The trans-mutative microbial framework called pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) can be distinguished by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs).
Anyhow, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV can avoid the host detection of their viral genome by adapting the double-membrane vesicle structure that lack pattern recognition receptors and begin to replicate in these vesicles.
Accessory protein 4a of MERS CoV may inhibit the initiation of IFN (IFN-alpha and beta has a protective action) over pointed connection with dsRNA at the level of MDA5 incitement.
Besides, ORF4a, ORF4b, ORF5, and membrane proteins of MERS CoV activation of IFN b promoter and nuclear transport of IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) may be inhibited by ORF4b, ORF5, ORF4a and membrane protein of MERS-CoV.
The antigen presentation of host cells can be down-regulated after coronavirus infection. Therefore, the destruction of immune evasion of coronavirus is vital in particular drug development and its treatment.
The authors are scholar at Institute of Pharmacy, Physiology and Pharmacology, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. Maria Daud Bhatti is the corresponding author.